Setlling Process¶
- Settling process depend on settling velocity, which varies according to the particulate material.
- a modelling strategy is proposed with a choice of some formulations for defining the settling velocity W_s for MUD variables. (Settling velocities : Modelling strategy).
Settling fluxes from water to sediment¶
- the settling fluxes which carry particles from the bottom layer to sediment are evaluated for each variable, according to their settling velocity and the bottom shear rate ((Deposit Processes)
Settling velocities : Modelling strategy¶
- If you are not using key_sedim_MUSTANG : settling velocity is defined by 2 parameters given by user in variable.dat : Defined simulated substances for each particulate variable (PART or NoCP) :
- minimum value : ws_free_min(iv)
- maximum value : ws_free_max(iv)
- If you are using key_sedim_MUSTANG : a modelling strategy is proposed with a choice of some formulations.
- Options and parameters are given by user in variable.dat for each particulate variable (MUD, PART or NoCP).(Definition of parameters for particulate-sediment substances in variable.dat)
- SAND variable have settling velocities W_s which depend on particle diameter.
- Settling velocity of MUD is defined by 2 notions : Free settling velocity and Hindered settling velocity.
- None constitutive SORBED variables have the same settling velocity as the associated constitutives particulate variable.
- For the none constitutive variables which are not sorbed on constitutive particulate variable (type NoCP), settling velocity is evaluated in the same manner as MUD variables.
Exemple of evolution and values of settling velocities issued from these different choices are presented below (Exemples of evolution of settling velocity according to different options)
in MARS, for variables which have high settling velocity, vertical transport is computed using several sub time step in order to avoid instabilities.
Definition of parameters for particulate-sediment substances in variable.dat¶
- particulate variables are defined in variable.dat : Defined simulated substances as :
- GRAV or SAND or MUDS or PART : constitutive variables (kg/m3)
- SORB or NoCP : non constitutive variables (X/m3)
For GRAV and SAND variables, only diameter of particles, critical stress of deposition and density of particle are given in variable.dat
- For MUDS, PART and NoCP
: settling velocity varies with time and space (Settling velocities : Modelling strategy) and 4 lines with 11 parameters are given in variable.dat
- 1 option for free velocity followed by 6 parameters
: minimum and maximum setling velocity (m/s) and :
- If ws_free_opt=0 (Ws constant) ==>> (1)=unused (2)= unused (3)=unused (4)=unused
- If ws_free_opt=1 (Van Leussen) ==>> (1)=c_factor (2)=c_exponent (3)=VL_a (4)=VL_b
- If ws_free_opt=2 (Winterwerp) ==>> (1)= Primary Particle Diameter (2)=aggregation factor (3)=breakup factor (4)=fractal dimension
- If ws_free_opt=3 (Wolanski) ==>> (1)= c_factor (2)=c_exponent (3)=unused (4)=unused
- 1 option for hindered velocity followed by 2 parameters :
- If ws_hind_opt=0 (no hindered settling) ==> (1)=unused (2)=unused
- If ws_hind_opt=1 (Scott) ==> (1)=phi_factor (2)=phi_exponent
- If ws_hind_opt=2 and ws_free_opt=2 (Winterwerp) ==> (1)=gel concentration (kg/m3) (2)=phi_exponent
- If ws_hind_opt=3 (Wolanski) ==> (1)=c_constant (2)=c_exponent
- diameter of particles, critical stress of deposition and density of particle are given after
For SORB variables, user must given the name of the associated constitutive particulate variable.
- Inital concentration in sediment is expressed as :
- gravel, sand, mud and PART : fraction of total initial sediment concentration (total=1)
- SORB (or NCSP) : unit/m3 of sediment
- DISS : unit of m3 of interstitial water
- For SAND variable only; 2 boolean are given in variable.dat :
- l_sand2D which is TRUE if this sand variable is treated as 2D variable (used only if key_sand2D)
- l_outsandrouse which is TRUE if you want to use a ROUSE profil reconstituted for output in water column (used only if ikey_sand2D and l_sand2D is TRUE for this variable)
Free settling velocity¶
4 options defined by a parameter (ws_free_opt) given by user in variable.dat : Defined simulated substances for each particulate variable (MUD, PART or NoCP). Some parameters values are proposed below.
Option free 0 : Constant settling velocity defined by minimum value (ws_free_min(iv)) and maximum value (ws_free_max(iv)) - aditional parameters are not used (ws_free_para(1:4)
Option free 1 : Formulation of Van Leussen, 1994
\(Ws=kC^m \frac{1+aG}{1+bG^2}\)
- \(k=0.0005\) =*ws_free_para(1)*
- \(m=1.2\) =*ws_free_para(2)*
- \(a=0.3\) =*ws_free_para(3)*
- \(b=0.09\) =*ws_free_para(4)*
Option free 2 : Formulation of Winterwerp, 1999
\(D_e=D_p+ \frac{k_aC}{k_b \sqrt{G}}\)\(Ws=\frac{1}{18} \frac{(\rho_s-\rho)g}{\mu} D_p^{3-n_f} D_e^{n_f-1}\)
- \(D_p=4.10^{-6}\) =*ws_free_para(13)*
- \(k_a=14.6\) =*ws_free_para(2)*
- \(k_b=30000\) =*ws_free_para(3)*
- \(n_f=2\) =*ws_free_para(4)*
Option free 3 : Wolanski et al., 1989 : include Hindered settling (ws_hind_opt must be = 3 also; otherwise error and stop)
\(Ws=k C^m\) * \(k=0.01\) =*ws_free_para(1)* * \(m=2.1\) =*ws_free_para(2)* * ws_free_para(3) and ws_free_para(4) not used
Hindered settling velocity¶
4 options defined by a parameter (ws_hind_opt) given by user in variable.dat : Defined simulated substances for each particulate variable (MUD, PART or NoCP)
Option hindered 0 : no hindered settling velocity
Option hindered 1 : Formulation of Scott, 1984
\(\Phi=\frac{SPM_{tot}}{cgel}\)\(Ws=Ws(1-\Phi)^m\)
- \(cgel=40\) =*ws_hind_para(1)*
- \(m=4.5\) =*ws_hind_para(2)*
Option hindered 2 : Winterwerp 2002
\(Ws=Ws(1-\Phi_v)^m \frac{(1-\Phi)}{1+2.5\Phi_v}\)if Option free = 2 \(\Longrightarrow \Phi_v=\Phi (\frac{D_e}{D_p})^{3-n_f}\)
- \(m=1\) =*ws_hind_para(2)*
if Option free \(\neq 2 \Longrightarrow \Phi_v=\frac{SPM_{tot}}{cgel}\)
- \(cgel=40\) =*ws_hind_para(1)*
- \(m=1\) =*ws_hind_para(2)*
Option hindered 3 : Wolanski et al., 1989
\(Ws=frac{Ws}{(C^2+b_w^2)^{m_w}}\)if Option free = 3
- \(b_w=2\) =*ws_hind_para(1)*
- \(m_w=1.46\) =*ws_hind_para(2)*
if Option free \(\neq 3\) : error and stop
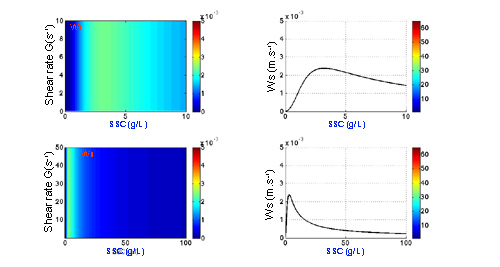
Exemples of evolution of settling velocity according to different options¶
Option free 1 and Option hindered 0 : 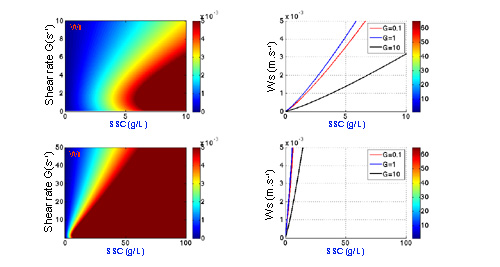
Option free 1 and Option hindered 1 : 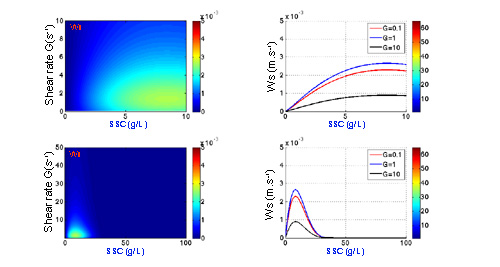
Option free 1 and Option hindered 2 : 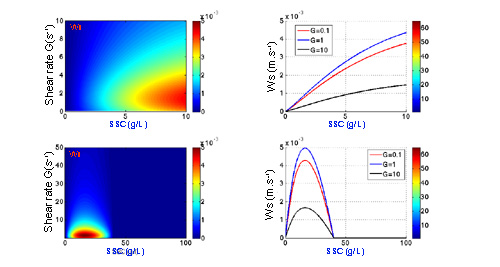
Option free 2 and Option hindered 1 : 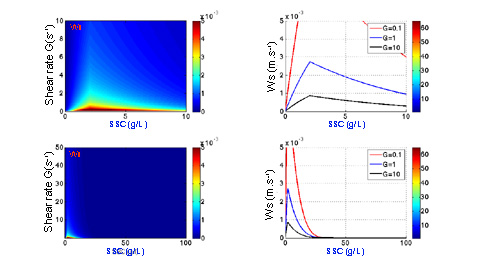
Option free 2 and Option hindered 2 : 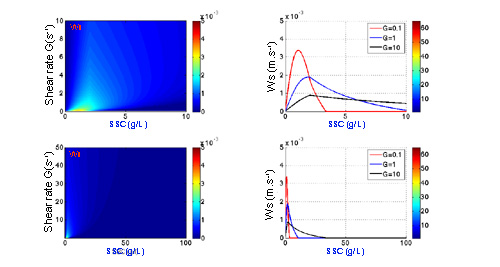
Option free 3 and Option hindered 3 :