Modulation of reaction kinetics in module MET&OR¶
Kinetic Modulation with Temperature (Arrhenius function)¶
The Arrhenius law corrects the kinetics of the reaction as a function of temperature. User can choose between two different types:
First Law called \(\theta\)
\(\mu_{T}=\mu_{T_{ref}} F_{Temp}\)\(F_{Temp}=\theta^{\frac{(T_T-{ref})}{\zeta}}\)avec :
- \(T_{ref}\) : reference temperature
- \(\mu_{T_{ref}}\) : kinetic max at reference temperature
- \(T\) : temperature at time t
- \(\theta\) : correction coefficient
- \(\zeta\) = 1 or 10 depending on law.
For chemical reactions, the law is often used with \(\zeta= 1\) and \(T_{ref}\) = 15 degC or 20 degC.For biological reactions, the dependence is reported in terms of \(Q_{10}\) which represents the ratio between reaction rates at 20 degC and at 10 degC; \(\theta\) is then set equal to \(Q_{10}\), and \(\zeta\) is equal to 10.Second Law called exponential law
\(\mu_{T}=\mu_{T_{ref}} F_{Temp}\)\(F_{Temp}=\theta e^{-(\frac{(T_T-{ref})}{\sigma})^2}\)avec :
- \(T_{ref}\) : reference temperature
- \(\mu_{T_{ref}}\) : kinetic max at reference temperature
- \(T\) : temperature at time t
- \(\sigma\) : deviation
- \(\theta\) = 1
Kinetic Limitation with a Monod function or an inhibiting function or with light radiation¶
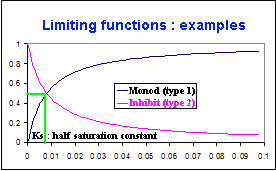
These two functions vary according to the concentration of the limiting variable.
For type Monod function : \(F_{L}\) approaches 0, if the concentration is less than Ks
The reaction does not occur or is reduced if the limiting variable is in low concentration.
For type Inhibit function, the higher the concentration of the limiting variable becomes,
the lower the reaction may develop. It is at full speed if the concentration is zero.
|
|
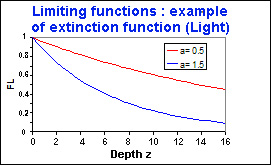
The third limiting function is a function of light,
It decreases with the depth according to an exponential law with an extinction coefficient
(here \(\chi=0.1\) )
|
|
Kinetic Limitation with a Monod
\(F_{L1}=\frac{C_{lim}}{C_{lim}+K_s}\)avec :
- \(F_{L1}\) : Limiting function (type 1 : Monod), [between 0 and 1 ]
- \(C_{lim}\) : Limiting concentration corresponding to this function and one reaction
- \(K_s\) : Half saturation constant
Kinetic Limitation with an inhibiting function
\(F_{L2}=\frac{K_s}{C_{lim}+K_s}\)avec :
- \(F_{L2}\) : Limiting function (type 2 : Inhibit), [between 0 and 1 ]
- \(C_{lim}\) : Limiting concentration corresponding to this function and one reaction
- \(K_s\) : Half saturation constant
Kinetic Limitation with light radiation
\(F_{L3}=e^{-a \chi z}\)avec :
- \(F_{L3}\) : Limiting function (type 3 : Extinction), [between 0 and 1 ]
- \(a\) : parameter corresponding to this function and one reaction
- \(\chi\) : extinction coefficient
- \(z\) : depth
